Designer
Designer is the main environment for creating, configuring, and managing the lifecycle of microservices within an organization. From this interface, users can define new microservices, edit existing ones, temporarily archive them, or permanently delete them according to operational needs.
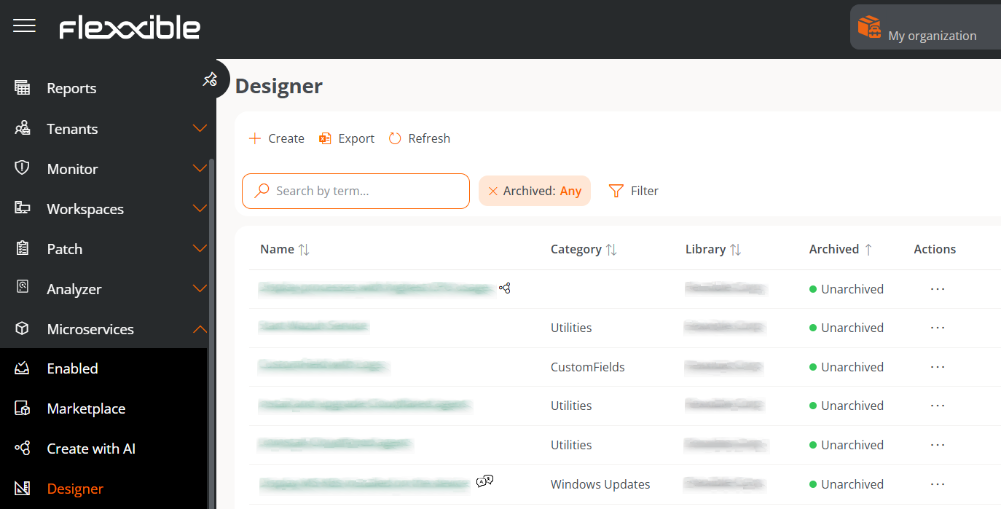
The list view shows a table with the created microservices, along with the following information:
-
Name. Enter the name of the microservice.
-
Category. Directory or group of microservices accessible from Workspaces. Categories must be predefined in Organization.
-
Library. Organization to which the microservice belongs.
-
Archived. Indicates whether the microservice is Archived or Active. Archived ones are not available for use, while active ones are.
-
Actions. Displays three options:
- View Details. Shows expanded information about the microservice.
- Edit. Allows you to modify the microservice's configuration.
- Archive / Activate. Opens a confirmation window to archive or activate the microservice, depending on its current state.
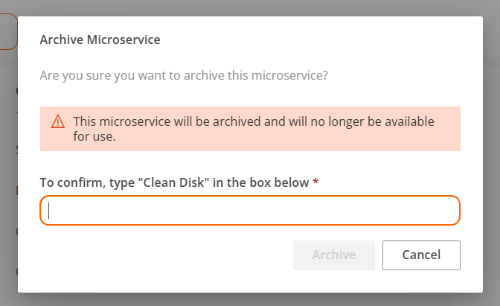
Confirmation window to archive a microservice:
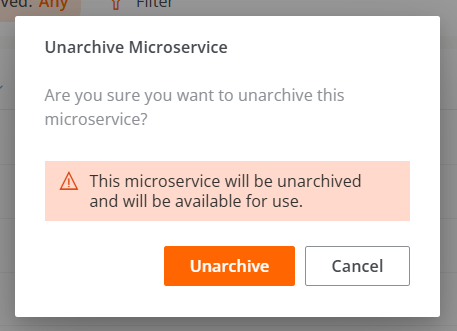
Confirmation window to activate a microservice:
Create new microservice
The process of creating a microservice is done through a wizard divided into four phases, guiding the user step-by-step until configuration is complete.
Phase 1 - Initial Configuration
- Access
Portal->Microservices->Designer. - Click on
New. - The wizard will open, asking to enter the following information:
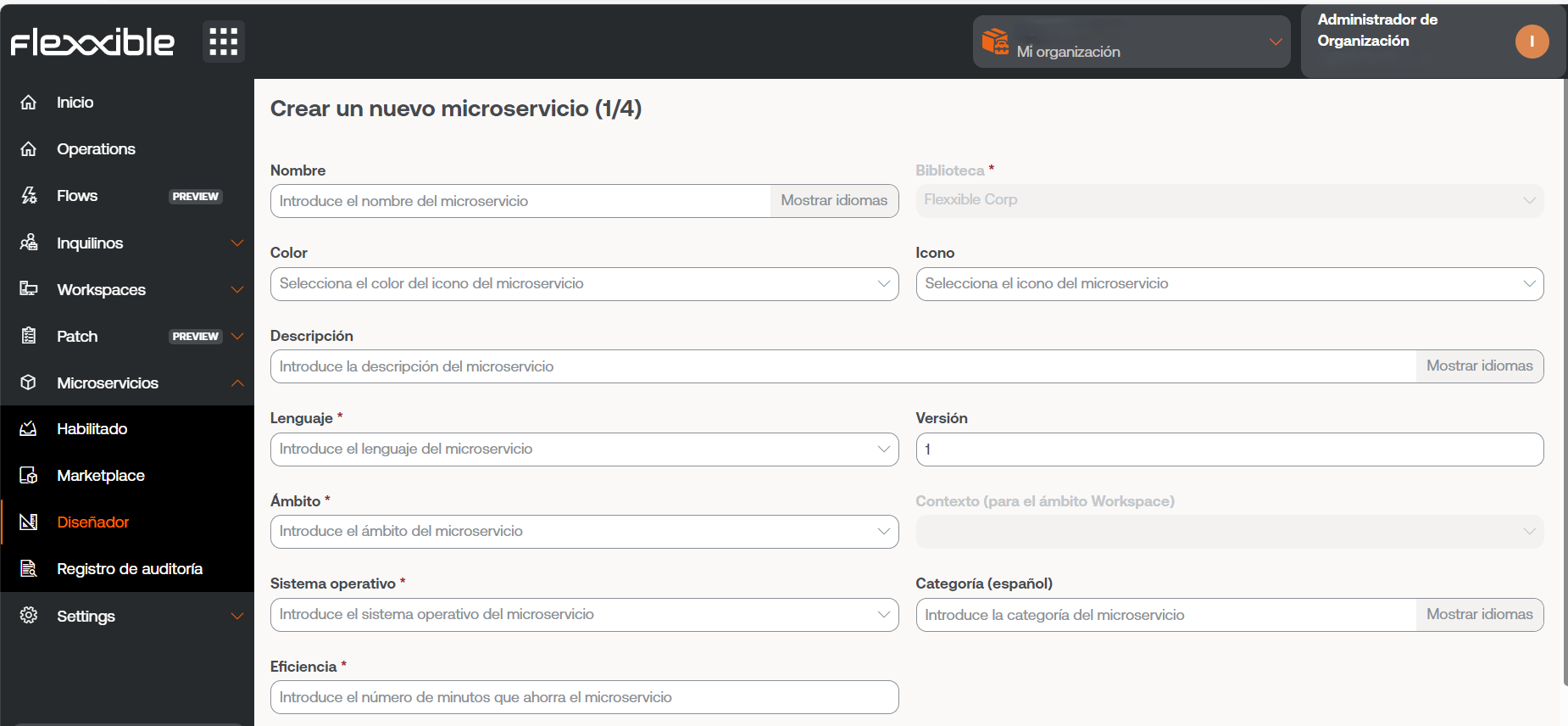
-
Name. Enter the name of the microservice.
-
Color. Color of the representative icon.
-
Icon. Type of associated icon.
-
Description. Brief explanation of its functionality.
-
Language. Programming language used.
-
Version. Version number.
-
Scope. Execution scope. You can select Workspace (context System or Session) or Platform.
-
Operating system. Operating system it is designed for.
-
Category. Directory or group of microservices accessible from Workspaces where it will be hosted. Categories must be predefined in Organization.
-
Efficiency. Number of minutes the user saves with each execution.
- Click
Next.
The name of a microservice configured for execution by the end user must not contain special characters like \ / : * ? " < > or specific language characters that may vary depending on the keyboard layout.
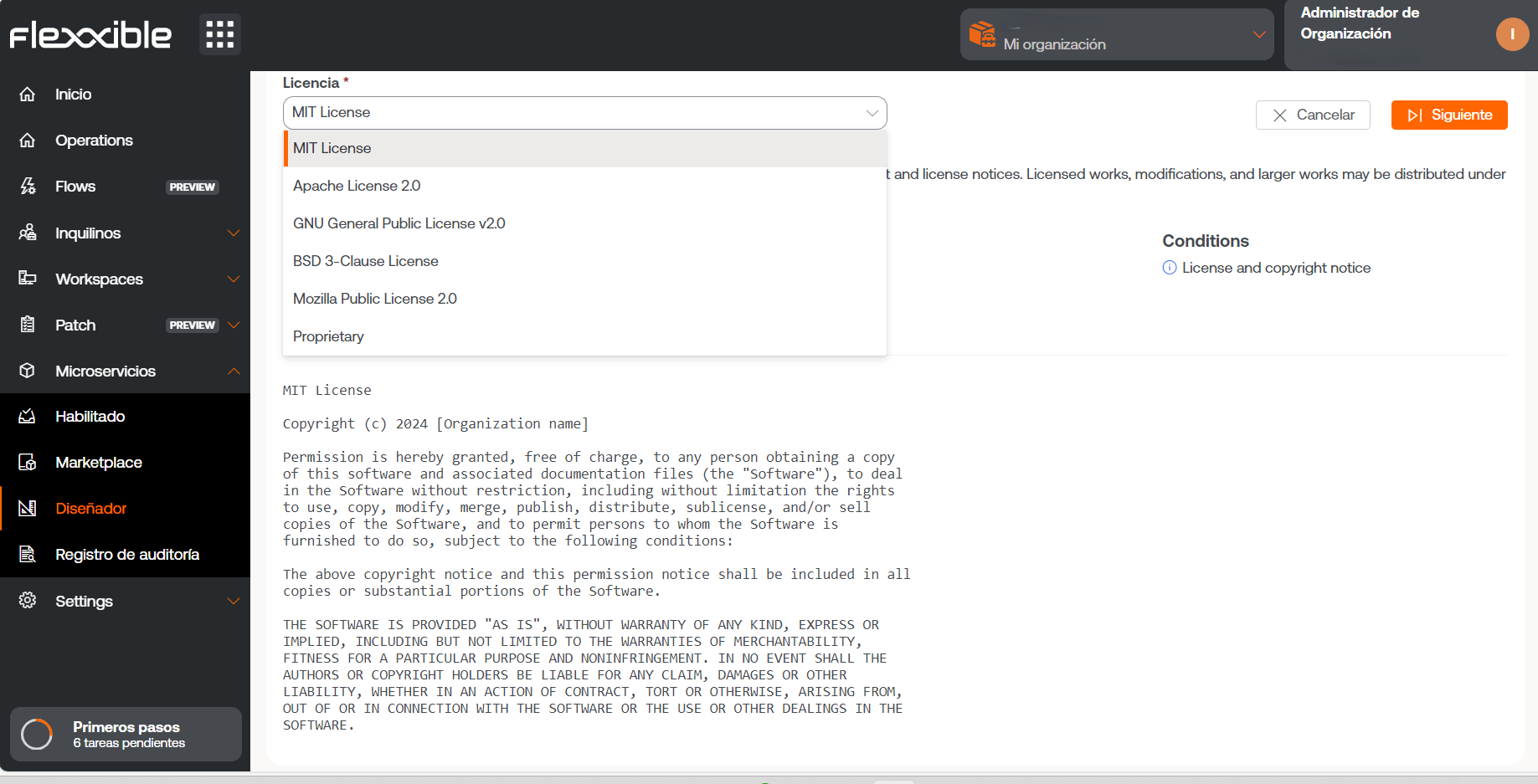
Phase 2 - License
- Choose from the dropdown options the type of license the microservice will have.
- Click
Next.
Phase 3 - README
- Enter the detailed description of the microservice in Markdown format.
- Click
Next.
To set a title with Markdown, simply start the line with # Title. Here are some examples of its syntax:
| Item | Markdown Syntax | Preview |
|---|---|---|
| Bold | **bold** | bold |
| Italic | *italic* | italic |
| List | - List item | - List item |
| Link | [text](url) | text |
| Image |  |  |
| Code | `code` | code |
Phase 4 - Code
- Enter the script of the microservice.
- Click
Nextto finish.
Once the phases are completed, the microservice will appear in the main table of the section.
Technical considerations
Although microservices allow the execution of any CMD or PowerShell command on Windows devices, the sent commands will be executed from the local administrator or the user session, depending on the assigned scope. This may mean that some cmdlets do not have the expected output in relation to the execution performed. For this reason, if you're developing a script in PowerShell, you must consider a series of points:
-
It is recommended that the installed version of PowerShell on the devices is the same as the one used to develop the microservices.
-
The microservices can be executed under the user session identity or from the local administrator.
-
Execution from the local manager. In
Scope, you can setWorkspacesorPlatform, which makes it very easy to interact with processes, services, and act with administrative permissions on the device, but it may complicate accessing specific user information or their session. -
Execution from user session. In
Scope, you can setSessions, which is very useful for accessing user information like the log, information contained in the profile, etc. It should be noted that the script will be executed with the permission level that the user has, so if the user is not a local administrator, there will be certain limitations when acting at the system level.
-
-
When you want to display a message in the microservice output, it is recommended to use the cmdlet "Write-Output" instead of "Write-Host".
-
The output of the execution can be consulted in the details of the job generated during the execution.
Enable a Microservice
Enable a Microservice:
- Access
Portal->Microservices->Designer. - Find the microservice in the list and click on it.
- Click the
Enablebutton (located in the upper right corner). - Once enabled, the microservice will be shown with a green dot in the Marketplace section.
Remove microservice
Before removing a microservice, it is necessary to consider the following conditions:
- Only microservices that have been previously archived can be removed.
- The microservice must not be active in any tenant.
- There cannot be any flow that has it assigned.
Once these requirements are met, you can proceed with the definitive removal of the microservice through the following steps:
-
Access
Portal->Microservices->Designer. -
In the microservices table, choose the desired item and click
Actions->Archive. -
Confirm the action in the pop-up window to complete the archiving.
-
Return to the table and click on the name of the microservice you just archived.
-
From the
Overviewtab, click theDeletebutton.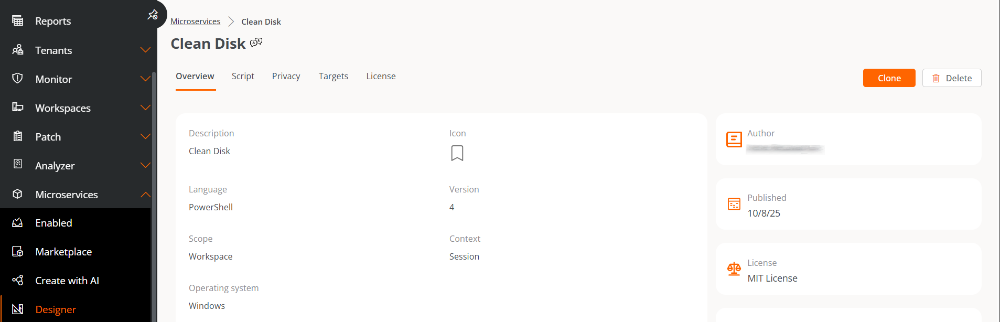
-
Confirm the deletion in the corresponding pop-up window.
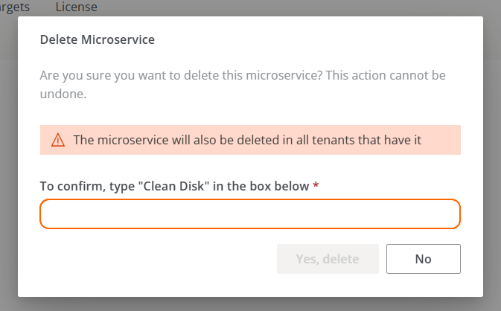
When a microservice is removed from the organization, it is also automatically removed from the list of microservices for its tenants.
The removal of a microservice is irreversible. Once deleted, it cannot be restored.