Microservices
Microservices are independent components that execute to prevent or solve frequent issues on devices, improve performance, or speed up tasks that might require a lot of time to do manually. Microservices can be executed autonomously or as part of a broader functionality within a system.
Microservices allows creating, enabling, and publishing microservices so they can be executed at the organizational level, as a prevention or self-remediation mechanism —through flows or alerts—, or directly by the end user.
This document describes in general terms what microservices are and how to execute them. The following articles provide more precise information about their behavior and configuration:
- Enabled. Describes how to activate a microservice for execution by an end user or from Workspaces.
- Marketplace. Shows the catalog of available microservices.
- Designer. Explains how to create new microservices and configure existing ones.
- Create with AI. Explain step-by-step how to generate microservices using natural language.
Features
Microservices offer a series of key advantages. The most relevant ones are described below:
Access to a centralized catalog
The available microservices are organized in the Marketplace section, where users can explore the catalog, select, and enable specific microservices according to the needs of their organization or particular use cases.
Creation of customized microservices
Portal allows users to easily create microservices via the Designer section. This tool guides the user, as long as they have the appropriate permissions, through all the necessary phases to build and configure their own microservice.
Execution scope configuration
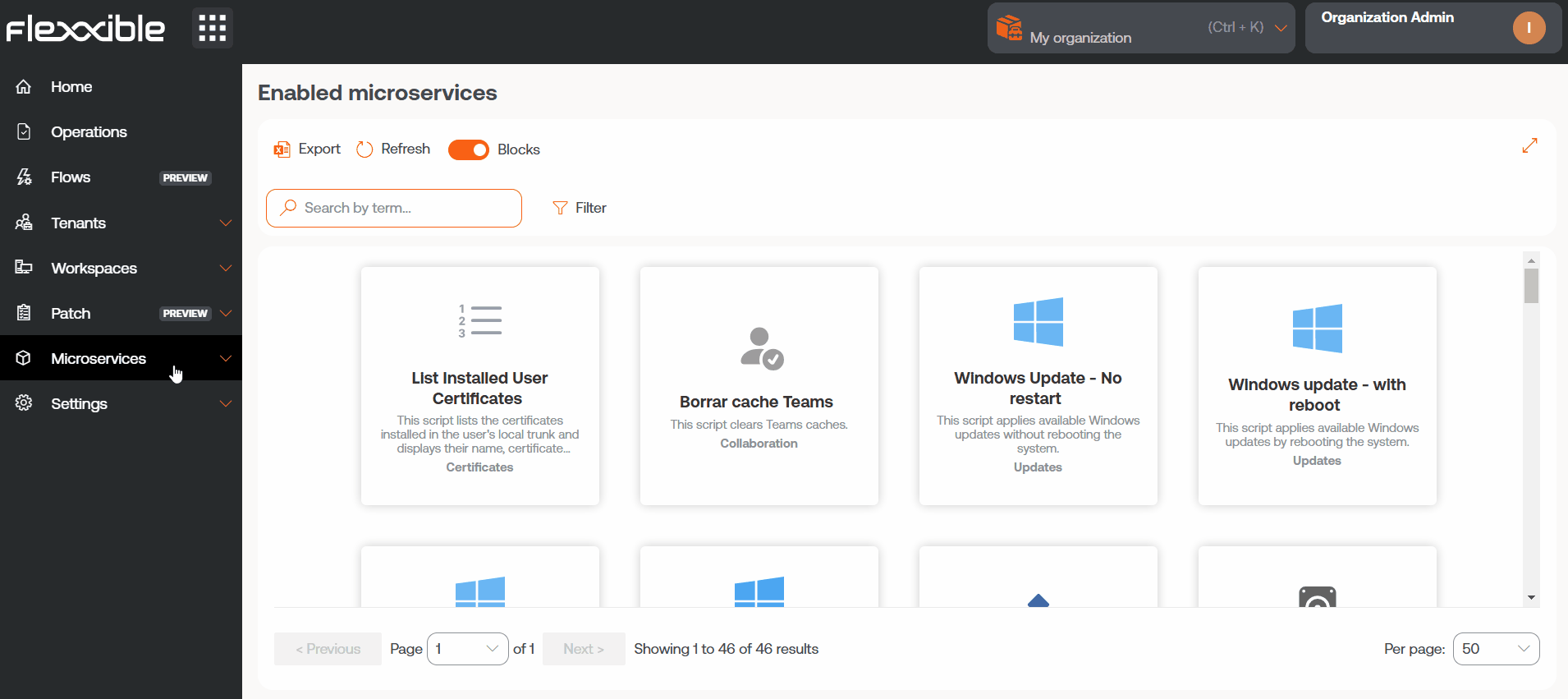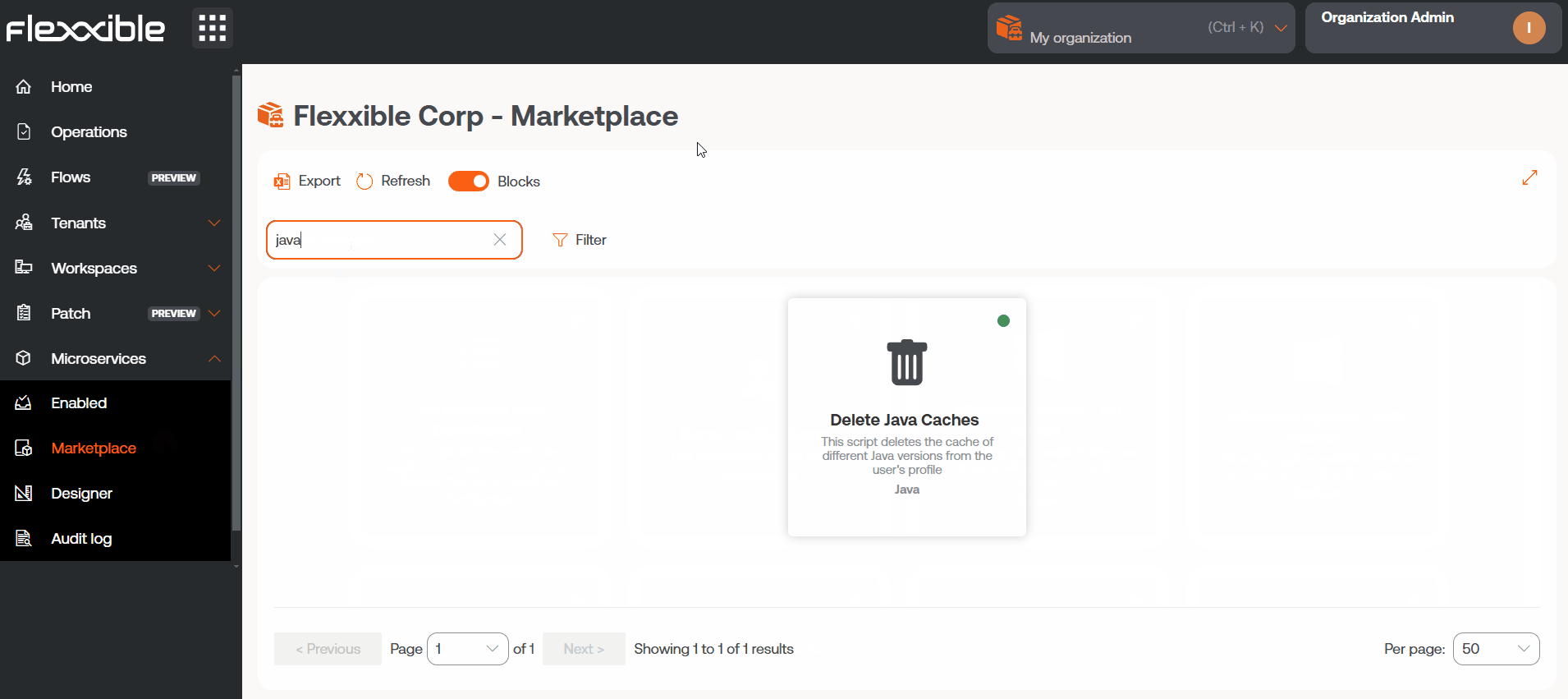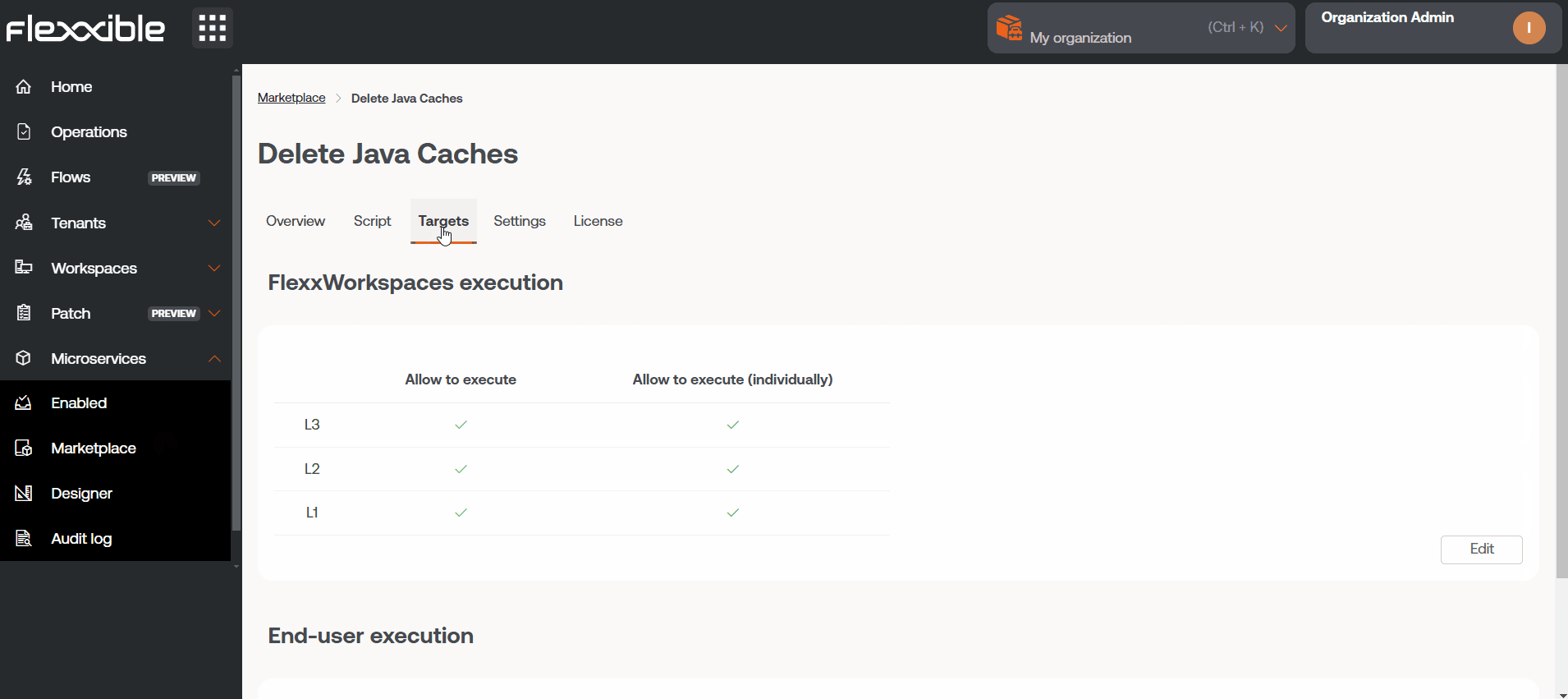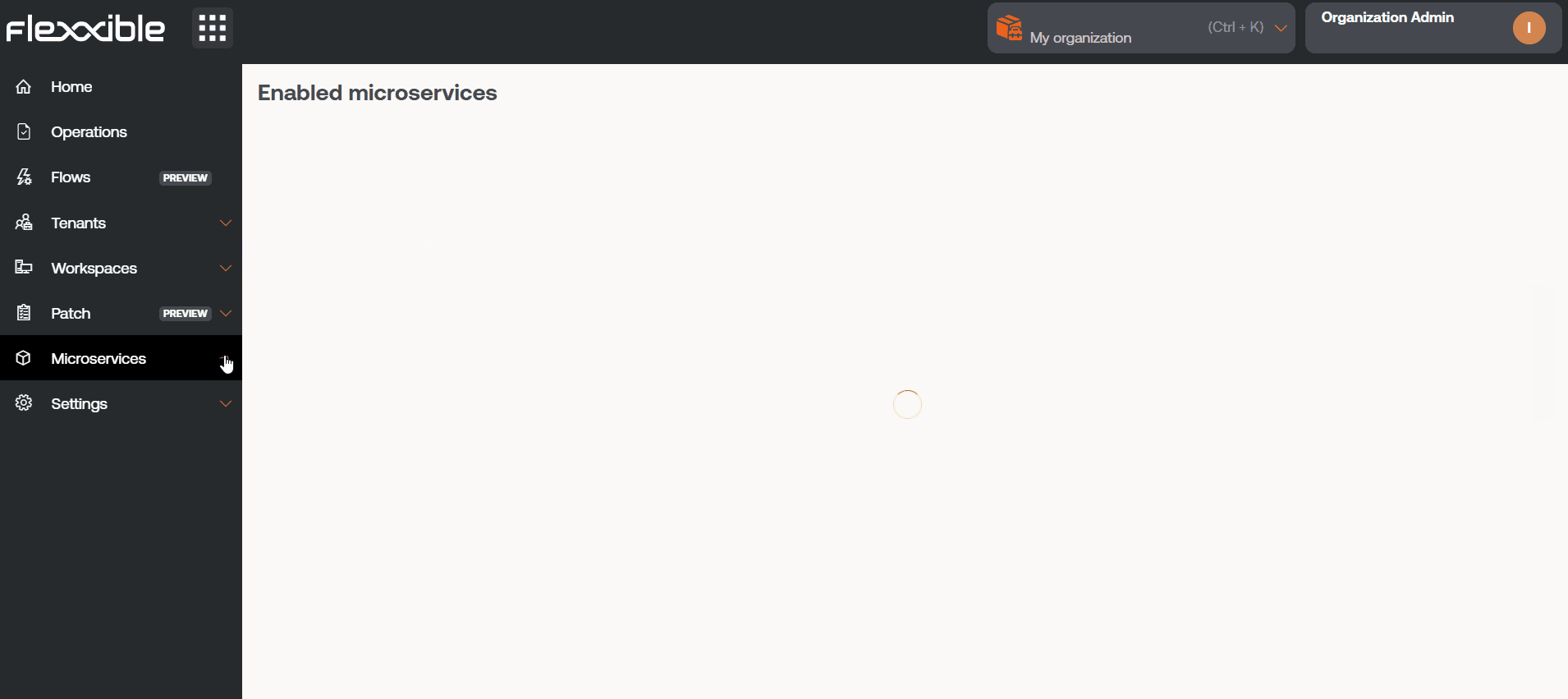
Each microservice can be defined to run in one of the following contexts, configurable from the Designer section.
Execution from the local administrator
It allows direct interaction with operating system services, processes, and other resources requiring elevated privileges. It's ideal for operations that must be executed with administrator permissions, but it may restrict access to specific user information or their session.
Execution from user session
Useful for accessing user information such as their log or information contained in their profile. The script will run with the permission level the user has, so if they do not have local administrator privileges, they will not be able to perform actions requiring system access.
Ways to consume microservices
Microservices can be created and enabled in Portal, and from there configured to be executed by the end user, launched via a flow or executed with automated or support actions from Workspaces.
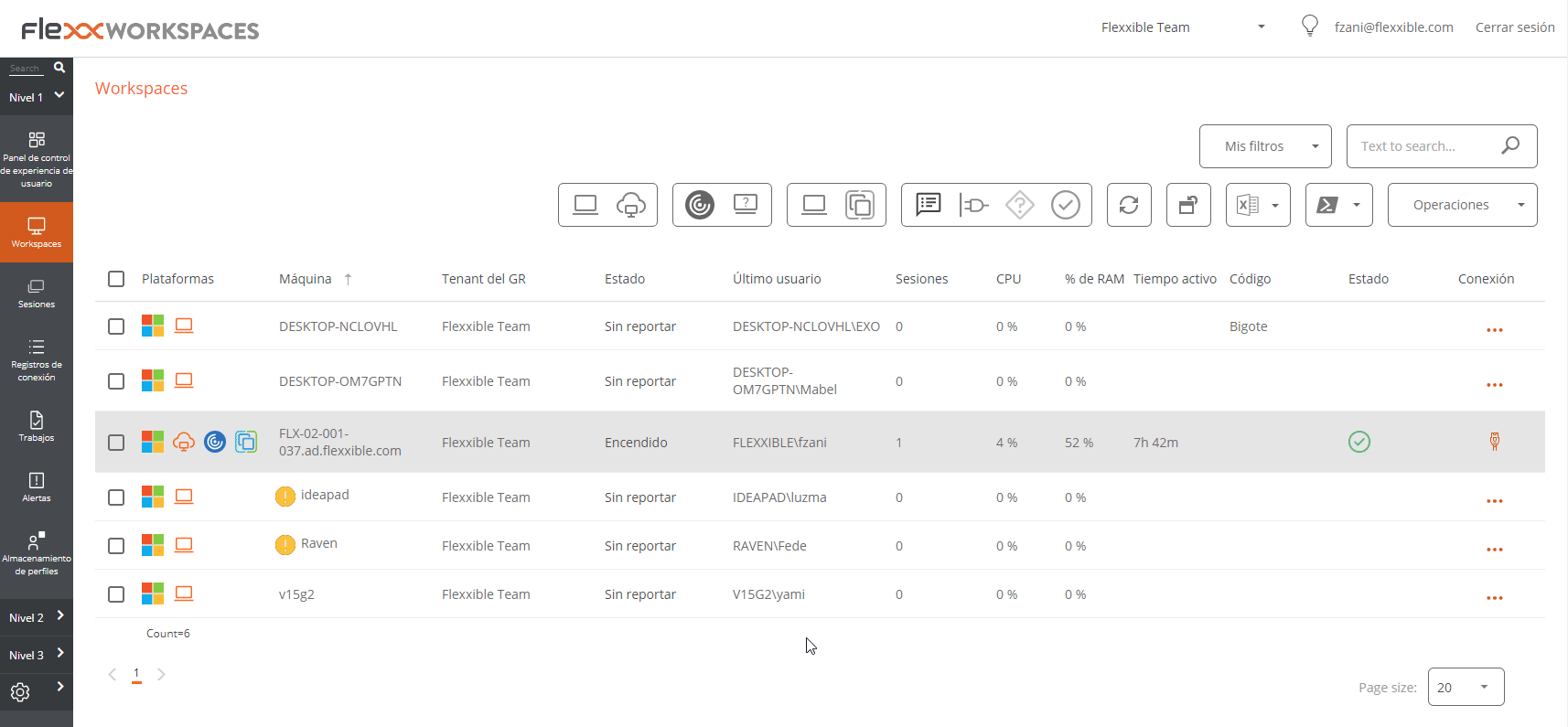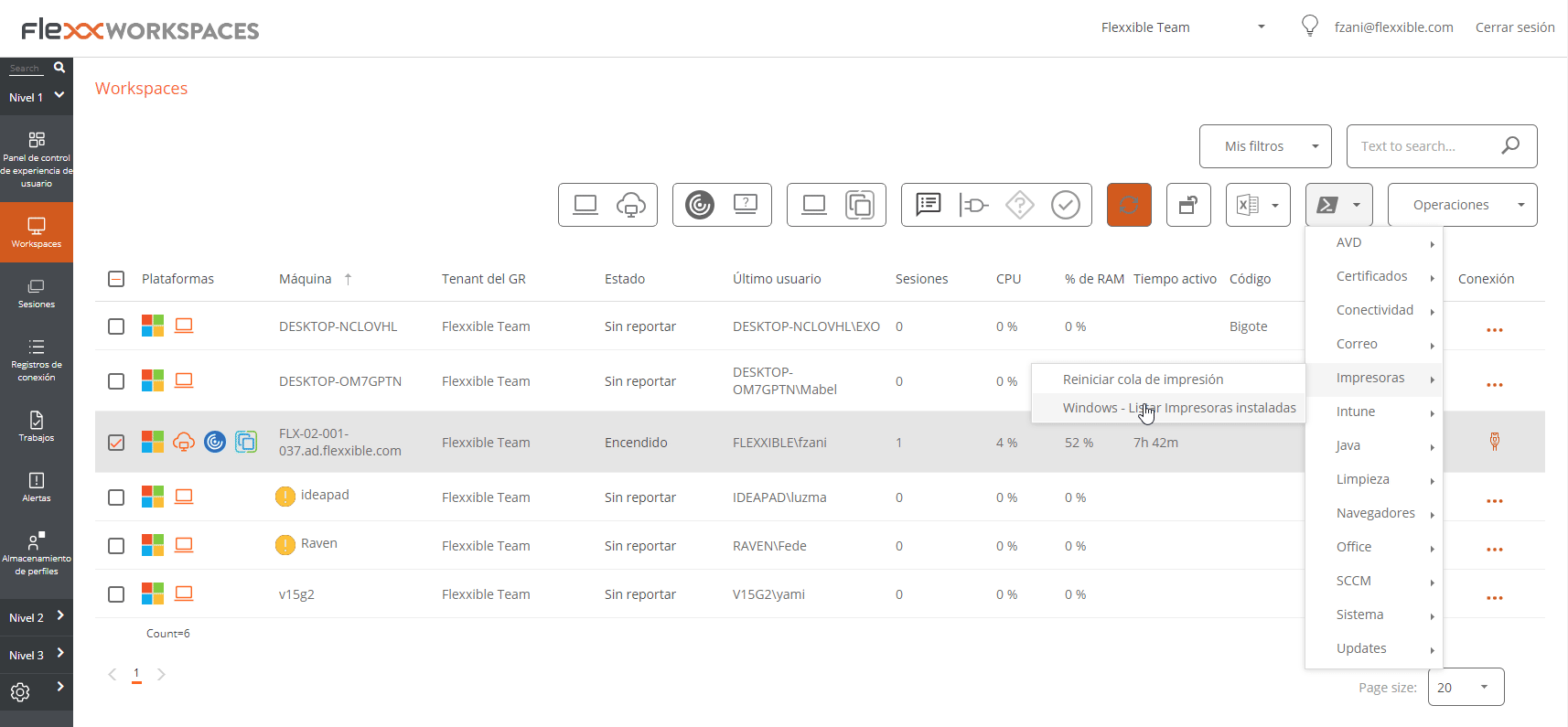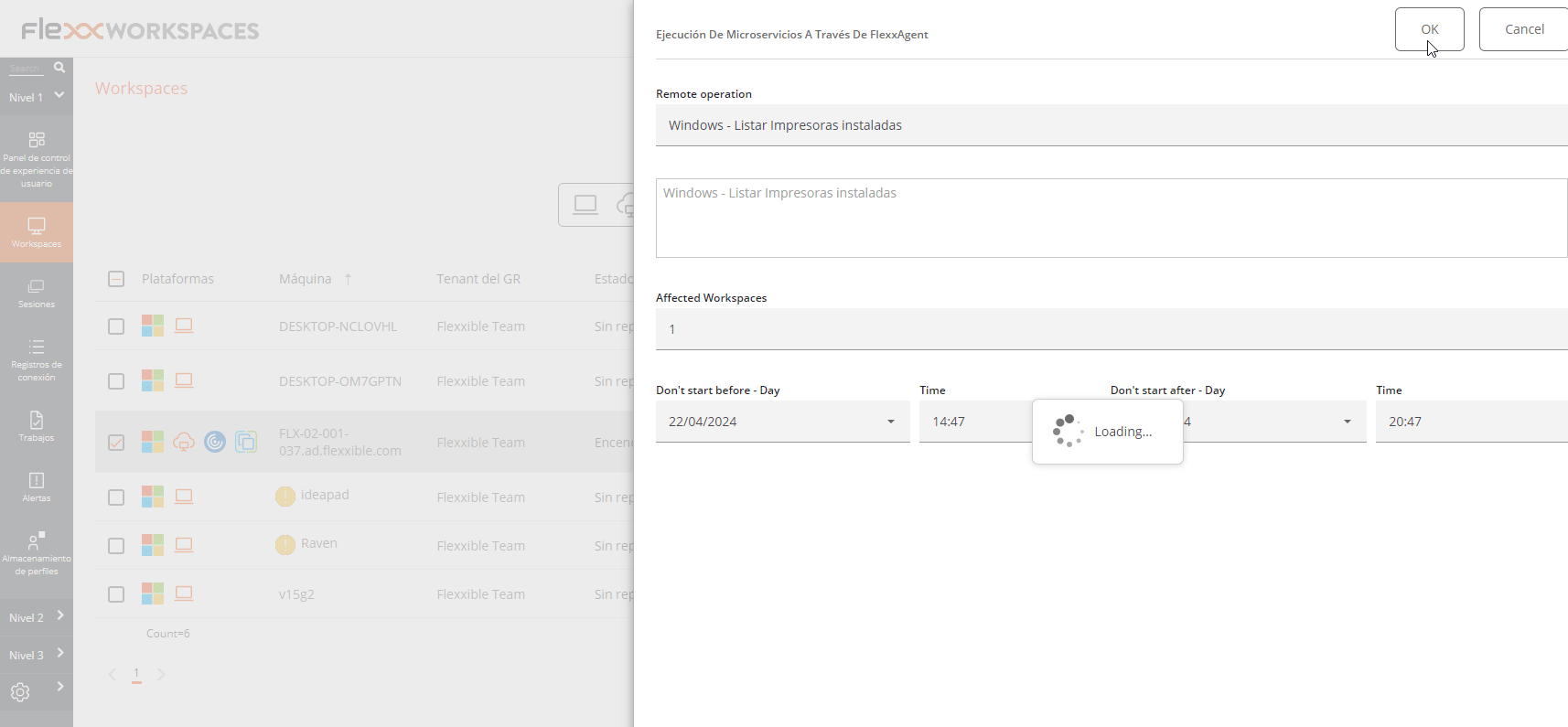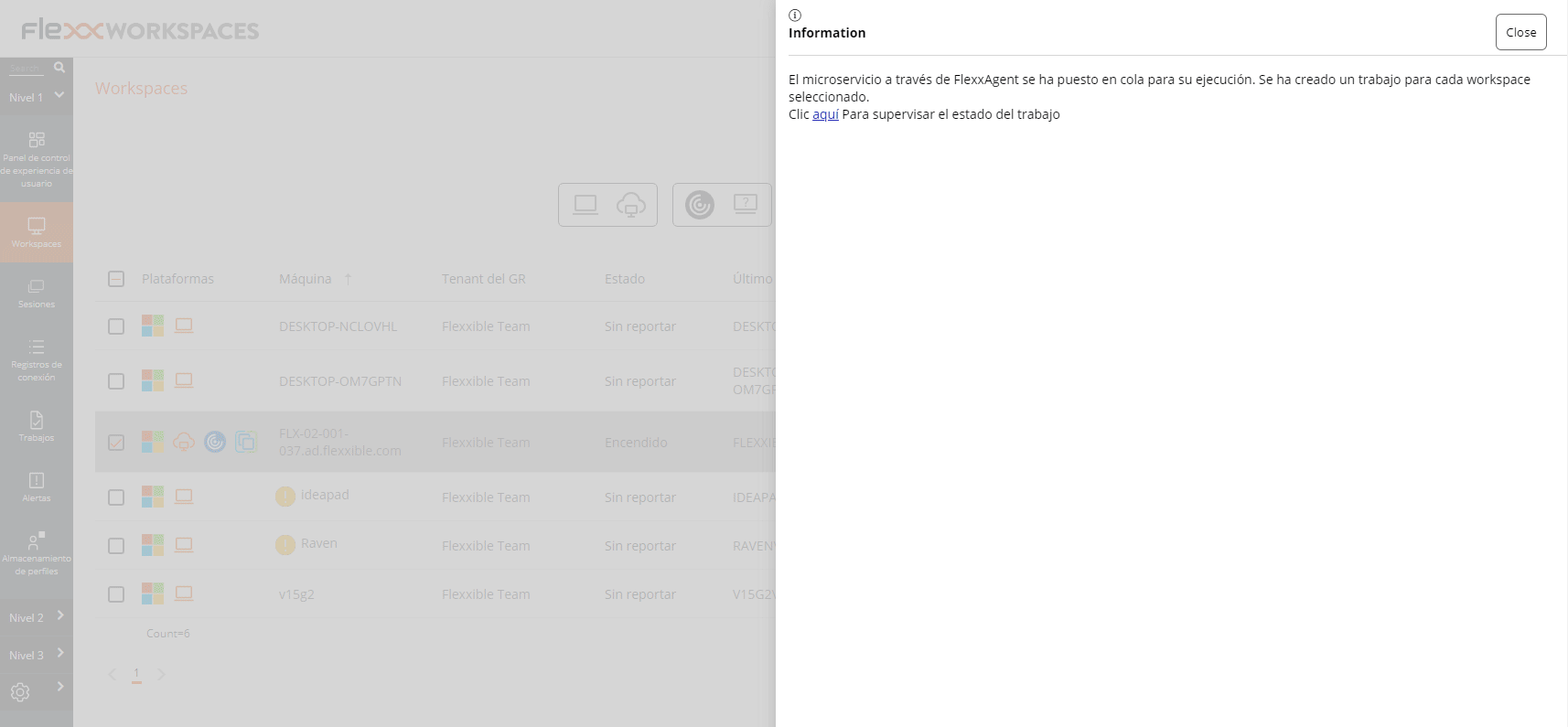
On-demand execution from Workspaces
Any microservice that has previously been enabled in Portal can be executed from Workspaces.
- Access the
Workspacesmodule ->WorkspacesorSessionssection. - Select the devices or sessions where you want to apply the microservice.
- In the top menu, click on the Microservices icon (
>_). - Select the microservice you want to execute.
Microservices will be visible in the Workspaces section when they have been configured to execute in the System context, and in the Sessions section when the configuration has selected the Session context.
You can manage the execution scope of the microservice and the permissions from the Designer section. It should be noted that the ability to execute certain microservices will depend on the user's role in the platform.
Scheduled execution through Flows
Flows is a feature that allows you to define automation sequences to execute scheduled actions on devices based on the evaluation of predefined logical conditions.
Its main characteristic is that it simplifies diagnostic actions and quickly resolves problems through the execution of a microservice.
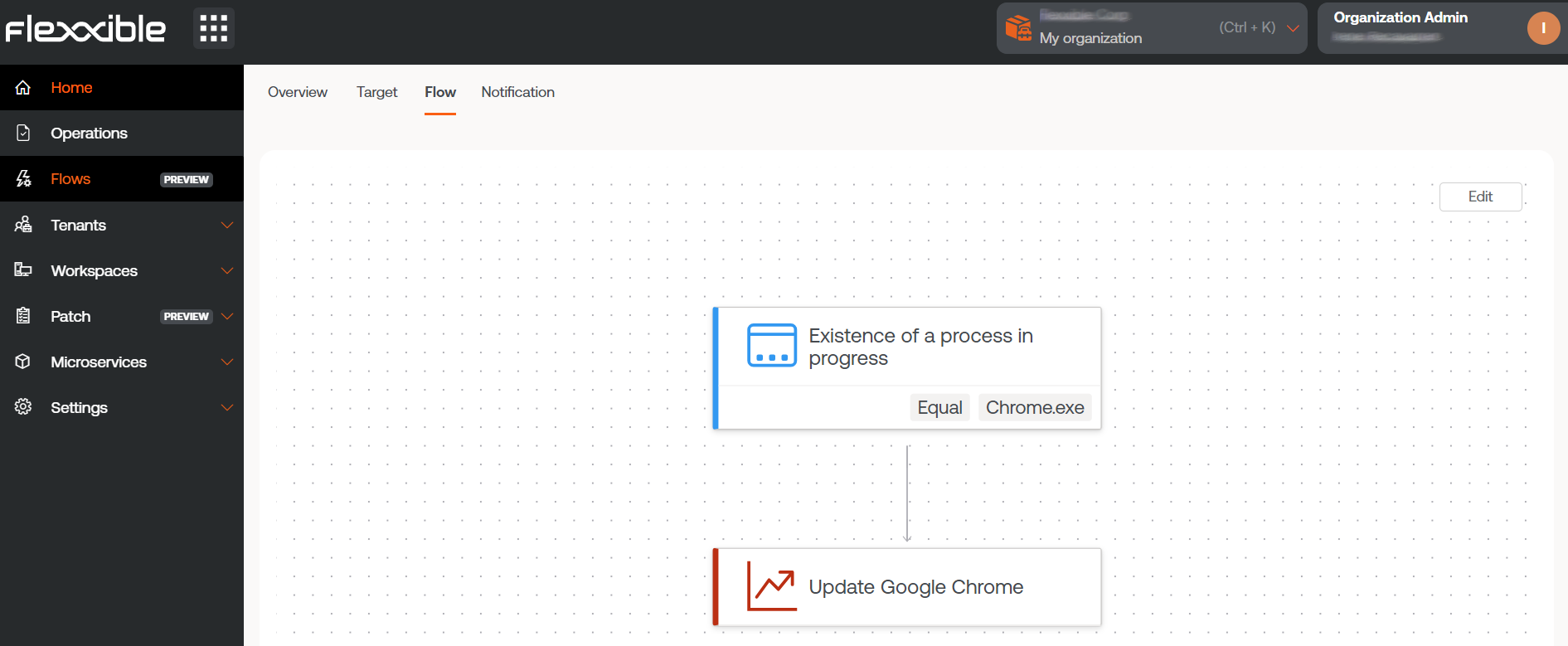
For more information on executing a microservice through a flow, please consult this guide.
Scheduled execution through Alert Settings
Through Alert Settings, it is possible to link events (event logs) to one or more microservices to prevent device issues or resolve problems promptly.
- Go to
Portal->Monitor->Alert Settings. - In the table, select an alert name to access its detailed information.
- In the left side menu, click on the
Microservicestab. - Click on
Link. - In the form, choose the microservice to link to the alert and the execution order (useful when linking more than one microservice).
- In the form, click on
Link.
For more information on linking an alert to a microservice, please refer to the Alert Settings documentation.
End-user execution
When a microservice is created, it is not automatically enabled for execution by the end user. To enable it, you need to complete the following configuration:
- Access
Portal->Microservices->Enabled. - Select a microservice from the list.
- In the
Targetstab, go to theEnd user executionsection. - Click on
Editand enableExecution by the end user.
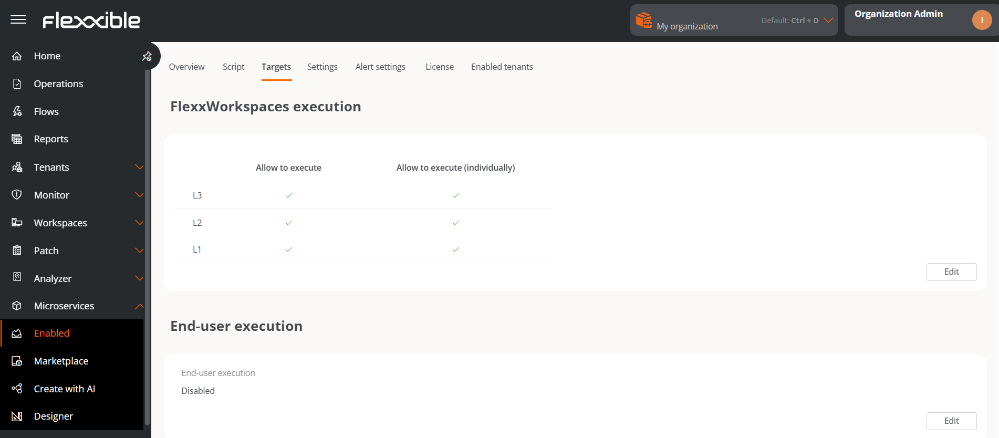
Next, optionally, you can configure notification reception.
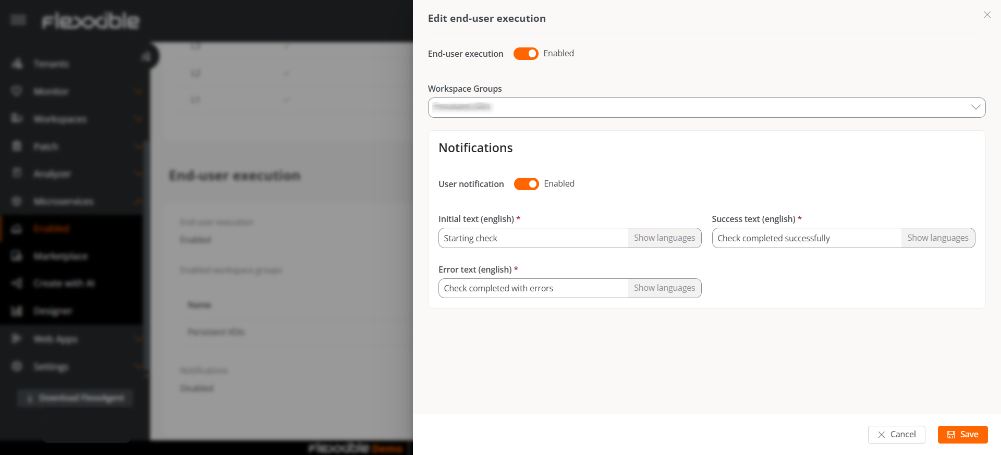
Notifications
This option lets you decide whether to notify the user when the microservice starts executing and when it finishes, whether successfully or with errors.
To do this, User Notification must be activated and the following fields completed:
- Initial text. Message displayed at the start of the microservice execution.
- Success text. Message displayed when execution completes successfully.
- Error text. Message displayed when execution ends with errors.
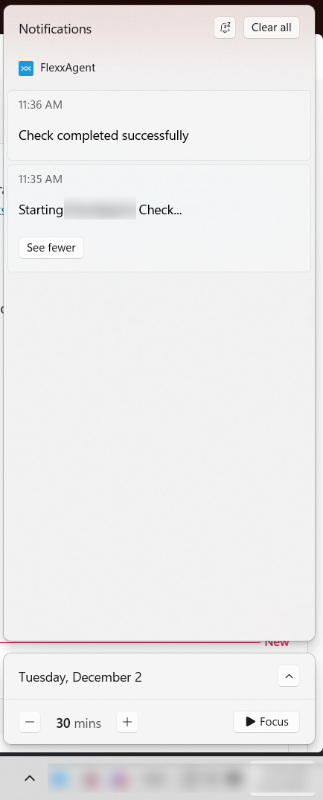
Notifications will appear in the Windows notification bar.
Rename the microservices folder
When microservices are enabled for execution by the end user, they are automatically added to a device folder called Flexxible; however, this name can be changed.
- Go to
Portal->Settings->Organization. - In the left sidebar, click on the
Microservicestab ->Edit microservices settings. - Rename the folder.
- Click on
Save.
The chosen name must be between 3 and 50 characters, and can only contain letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores.
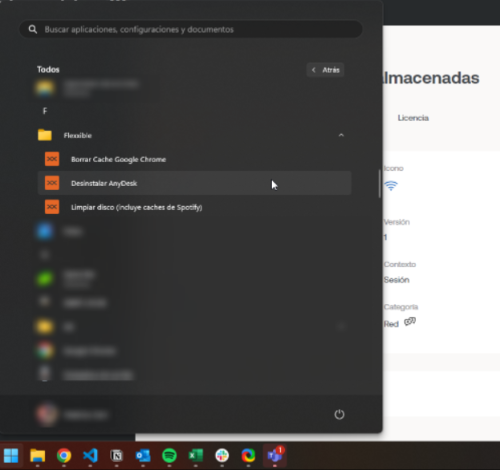
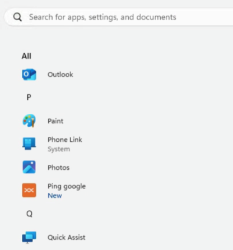
If the device has Windows 11 as the operating system and only one microservice is enabled for an end user, the folder will not be displayed; instead, only the microservice icon will be visible in the Start menu.
For more information on how to enable a microservice for the end user, please refer to this guide.